The number of possible stereoisomers for the products.
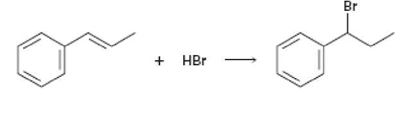
Methyl vinyl hbr reaction.
If methanol reacting as water would and if this reaction follows a typical mechanism of electrophilic addition what would be the expected product.
Hbr dmpu was shown to be very useful in other bromination reactions.
Click here to get an answer to your question 3 methyl pent 2 ene on reaction with hbr in presence of peroxide forms an addition product.
Alx 3 inx 3 nbx 5 gax 3 fex 3 snx 4 sulfonyl halides boron halides phosphorus halides or silicon halides scheme 2 which either require special handling or produce large amounts of side.
Methyl vinyl ether can be made by reaction of acetylene and methanol in presence of a base.
In the following reaction of the addition of hbr to 1 methyl 1 vinylcyclopentane 1 one of the major products formed is 1 bromo 1 isopropylcyclopentane 2.
This mode of reactivity is analogous to the way vinyl acetate.
The mechanism for this reaction involves the formation of intermediate a which is converted into intermediate b and finally product 2 is formed.
Methyl vinyl ether is a very reactive gas.
S n 1 reaction.
It is hydrolysed rapidly by dilute acids at room temperature to give methanol and aldehyde.
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate.
What type of reaction is this.
Vinyl ether 50 1 20 g 0 007 mol was dissolved in acetic acid 5 ml and warmed to 40 c.
Methyl vinyl ether h 2 c h o c h 3 reacts with b r 2 c h 3 o h.
This last reaction type is also known as the cloke wilson rearrangement.
After the addition was complete the temperature was raised to 55 c for 30 min.
The reason has to be explained for formation of racemic 3 bromo3 methylhexane when the reaction of hbr with r 3 methyl 3 hexanol.
Answer to reaction of methyl venyl ketone with hbr.
For example typical halogenating reagents employed in organic synthesis are gaseous hydrogen halides metal halides e g.
However under anhydrous conditions at room temperature it undergoes many addition reactions at the double bond electrophilic addition reaction more favourable.
It is prone to polymerization leading to formation of polyvinyl ethers polymerization is typically initiated with lewis acids such as boron trifluoride.
The mechanistic discussion on whether the vinylcyclopropane rearrangement proceeds through a diradical mediated two step or a fully concerted orbital symmetry controlled mechanism has been going on for more than half a century.
The alkene portion of the molecule is reactive in many ways.